
GROW GUIDE
Bell Pepper
Capsicum annuum
Plant Description
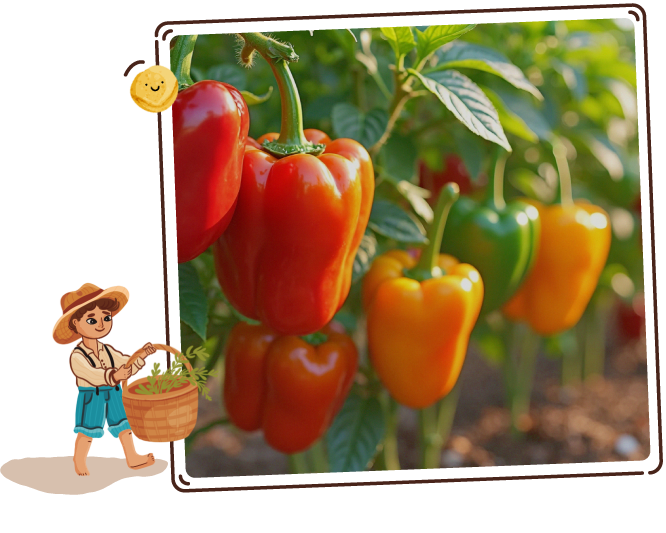

Bell Pepper
Technically a fruit, it has a smooth, glossy skin that comes in a spectrum of colors—from deep red to bright yellow and green.
This versatile food, known for its crisp texture and mild, subtly sweet flavor, is a popular choice for salads, stir-fries, and roasting, adding a fresh crunch and a burst of color to any dish.
Quick Facts:
-

Sun Requirements
Full Sun
-

Days To Sprout
7-14 Days
-

Days To Harvest
60-90 Days
-

Plant Spacing
18-24"
-

Seeds Per Hole
2
-

Planting Depth
1/4"
Best Planting Locations
-
Sunny Garden Beds
Bell peppers thrive in full sunlight with rich, well-draining soil, making sunny garden beds an ideal location.
-

Roomy Containers
Perfect for patios or balconies, containers offer control over soil and allow peppers to be moved to follow sunlight.
-

Greenhouses
A controlled environment with consistent warmth and humidity, promoting healthy pepper growth year-round.
-

Raised Beds
Offering improved drainage and warmth, raised beds are excellent for cultivating strong, productive bell pepper plants outdoors.
Getting Started

-
1
Find the Spot
Bell peppers thrive in warmth and full sunlight. Choose a sunny spot that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight each day. If growing indoors, place them near a south-facing window or use grow lights to ensure they get ample light.
-
2
Prep the Soil & Fertilizer
Use well-draining, fertile soil that retains moisture without becoming waterlogged. Enrich the soil with compost or aged manure.
Bell peppers benefit from a balanced, slow-release fertilizer at planting and a mid-season boost of low-nitrogen fertilizer for better fruiting.
-
3
Plant the Seeds
Plant 2 bell pepper seeds 1/4 inch deep in pots or directly in the ground. During germination, keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged, and place in a warm, bright location.
Maintain soil temperatures between 75° to 85°F for successful germination. Once seedlings appear, space them about 18-24 inches apart to allow ample room for growth.
Good Neighbors:
-

Marigolds:
Marigold flowers release chemicals that help fight harmful soil nematodes which can affect pepper plants
-

Carrots:
Don't compete for nutrients; carrots help retain soil moisture, suppress weeds and provide shade
-

Onions:
Onions deter aphids, cabbage worms, and other pests and do not compete for the same nutrients
-

Basil:
Basil thrives in similar conditions and helps repel pests like aphids and thrips
-

Nasturtium:
Act as a trap crop, attracting aphids away from bell peppers
Enemy Plants:
-

Bush Beans & Fennel:
Deplete nutrients in soil, stunting pepper growth
-

Broccoli:
Prefer different soil conditions & can deter pepper growth
Attractants:
-

Aphids, Flea Beetles, Thrips & Pepper Maggots:
Feed on various parts of the pepper plant
Repellents:
-

Deer:
Bitter taste, unappealing leaves
Best Time to Plant
USDA Hardiness Zones
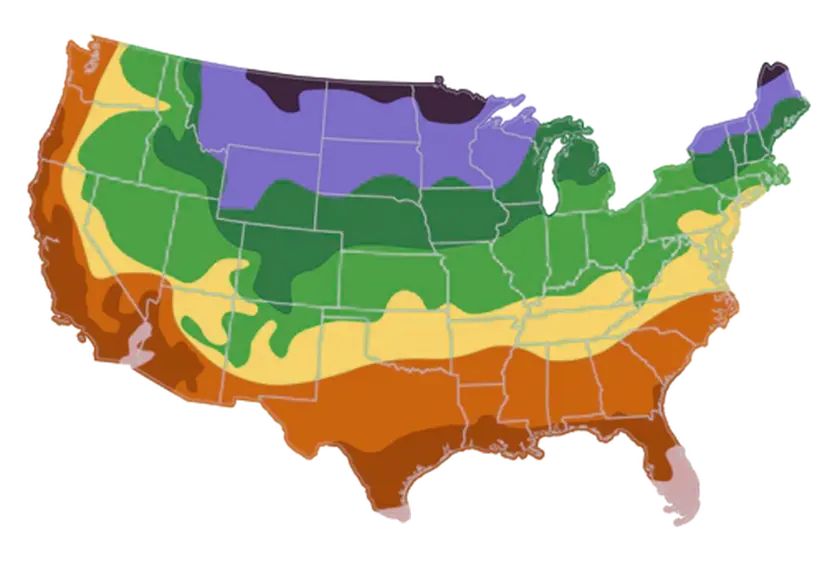
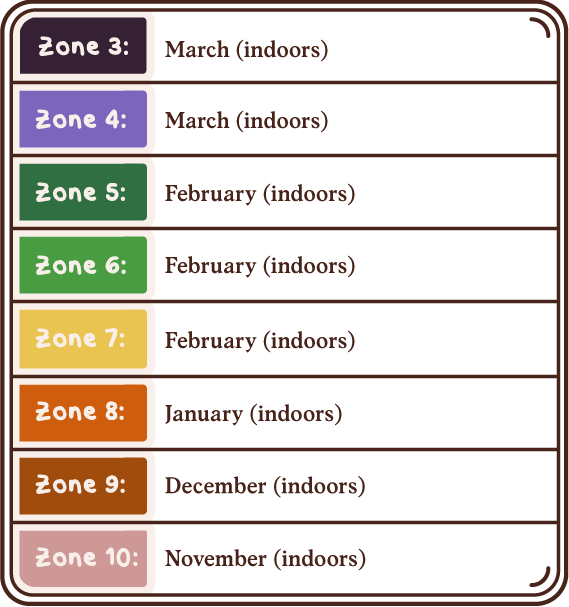
Day to Day Maintenance

-
Watering
Keep the soil consistently moist, but never leave soggy. Allow the soil to dry slightly between waterings. Water at the base of the plant to prevent fungal issues.
-
Pruning
Once the plant reaches about 8 inches in height, pinch off any small flowers or weak branches. Pruning helps direct energy to fruit production and encourages a sturdier, more productive plant. Remove any damaged or diseased leaves as they appear.
The Harvest

-
Gathering
Harvest bell peppers when they are 3-4 inches and have reached their mature color and size. Gently twist or cut the pepper from the stem.
-
Pick your peppers on a dry day or in the morning after the dew has dried. Working on wet plants can damage the foliage or spread disease. The peppers should be easy to pull off the plant. If you encounter resistance, give them a few more days to mature. A ripe bell pepper will feel heavy for its size.
Favorite Uses
-

Stir-fries
-
Pizza
-
Fajitas
-
Salad
-
Snacking


How to Store
-
Room Temperature
Duration: 3-5 days
Location: On countertop away from direct sunlight
Method: Store bell peppers whole, unwashed, and in a dry spot at room temperature if you plan to use them soon. Avoid cutting or bruising the peppers, as this can cause them to spoil faster.
-

Refrigeration
Duration: 1-2 weeks
Location: Store in the refrigerator crisper drawer
Method: Place whole, unwashed bell peppers in a plastic bag with holes or a produce bag in the crisper drawer to maintain moisture and prevent them from drying out. Once cut, store in an airtight container with a damp paper towel.
-

Freezing
Duration: Up to 6 months
Location: Store in the freezer
Method (Whole or Sliced): Wash, remove seeds, and slice or chop the peppers as desired. Arrange pieces in a single layer on a baking sheet, freeze until solid, then transfer to a freezer-safe bag or container for long-term storage.
-

Pickling
Duration: Up to one year
Location: Cool, dark pantry or refrigerated after opening
Method: Slice or chop bell peppers and immerse them in a vinegar-based brine. Once pickled, they can be stored in sterilized jars and used as a topping or ingredient in various dishes.
Fun Facts

-
Ripening Mystery
Green bell peppers are simply unripe versions of red, yellow, or orange peppers. As they ripen, their color changes, and their flavor becomes sweeter and milder.
-
Botanical Classification
Despite commonly being treated as vegetables in cooking, bell peppers are botanically classified as fruits because they contain seeds and develop from the flowering part of the plant.
-
Not-So-Spicy Cousins
Although they belong to the same family as chili peppers, bell peppers are completely mild. They lack capsaicin, the compound responsible for spiciness, making them a favorite for those who prefer a sweet, crunchy bite.
-
Nutritional Powerhouse
Bell peppers are packed with nutrients, boasting the highest levels of Vitamin C of any fruit or vegetable—three times more than oranges! A large red bell pepper can provide over 300% of your daily Vitamin C requirement.
Subscribe to our Newsletter: "The Small Garden Chronicles"
Where curious growers gather for garden inspiration.













