
GROW GUIDE
Ghost Pepper
Capsicum chinense
Plant Description
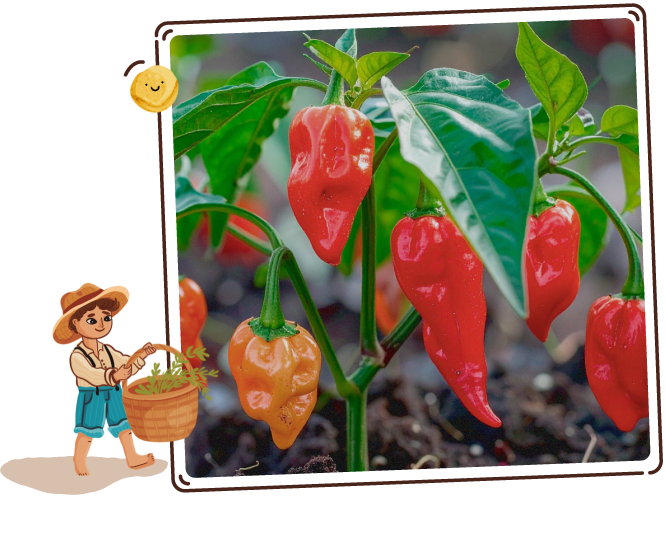

Ghost Pepper
A fiery chili plant recognized for its wrinkled, tapered pods that ripen from green to a vibrant red or orange hue.
This legendary pepper, native to Northeast India, is renowned for its intense heat and smoky-sweet undertones, making it a prized ingredient for spice enthusiasts and daring culinary creations.
Quick Facts:
-

Sun Requirements
Full Sun
-

Days To Sprout
21-28 Days
-

Days To Harvest
121-150 Days
-

Plant Spacing
18-24"
-

Seeds Per Hole
2
-

Planting Depth
1/4"
Best Planting Locations
-

Garden Beds
Best for warm climates with well-draining soil and ample sunlight.
-

Greenhouses
Provide consistent heat and humidity for optimal year-round growth.
-

Indoors
Thrives under grow lights, ensuring warmth and extended growing seasons.
-

Containers
Perfect for patios, offering mobility and controlled soil conditions.
Getting Started

-
1
Find the Spot
Thrives in heat and full sun. Choose a warm, sheltered spot with at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Indoors, a south-facing window or grow lights provide the best conditions.
-
2
Prep the Soil & Fertilizer
Use well-draining, nutrient-rich soil with good aeration. Ghost peppers thrive in slightly sandy or loamy soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8. Before planting, mix in compost or well-rotted manure to improve fertility. A balanced, slow-release fertilizer high in potassium and phosphorus will support strong root development and fruit production.
-
3
Plant the Seeds
Plant 2 seeds 1/4 inch deep in well-draining, nutrient-rich soil. Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy during germination, maintaining an ideal soil temperature of 80° to 90°F.
Once established, space plants 18–24 inches apart to allow for proper airflow and growth.
Good Neighbors:
-

Basil:
Enhances flavor of peppers & deters pests like aphids
-

Marigold:
Attracts beneficial insects like ladybugs and deters nematodes which damage pepper roots
-

Garlic:
Garlic repels aphids, spider mites, and other pests
-

Onion:
Onions deter aphids and other insect pests
-

Spinach:
Spinach helps shade the soil, retain moisture, and suppress weeds
Enemy Plants:
-

Fennel:
Releases compounds that inhibit the growth of peppers
-

Beans:
Can compete for nutrients and potentially spread diseases to peppers
Attractants:
-

Aphids & Spider Mites:
Feed on the leaves
Repellents:
-

Squirrels:
Repelled by the capsaicin in the peppers
-

Rabbits
Repelled by the capsaicin in the peppers
Best Time to Plant
USDA Hardiness Zones
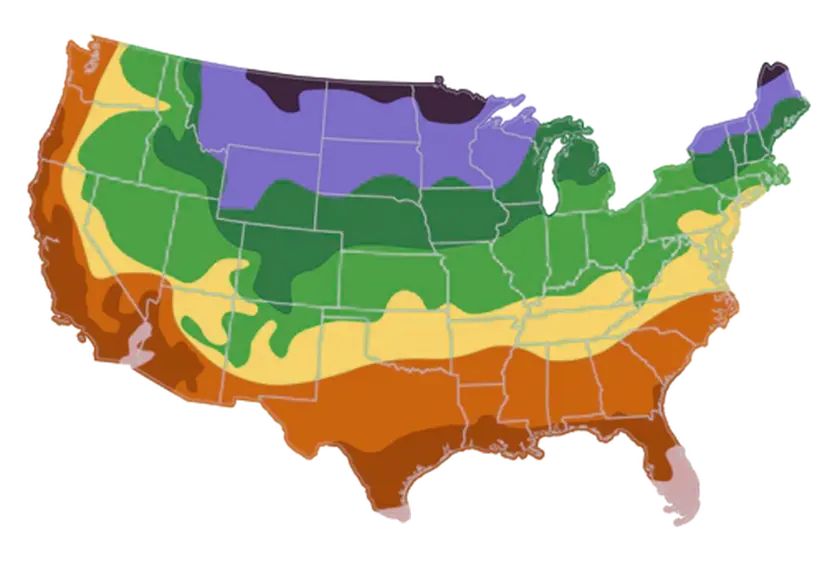
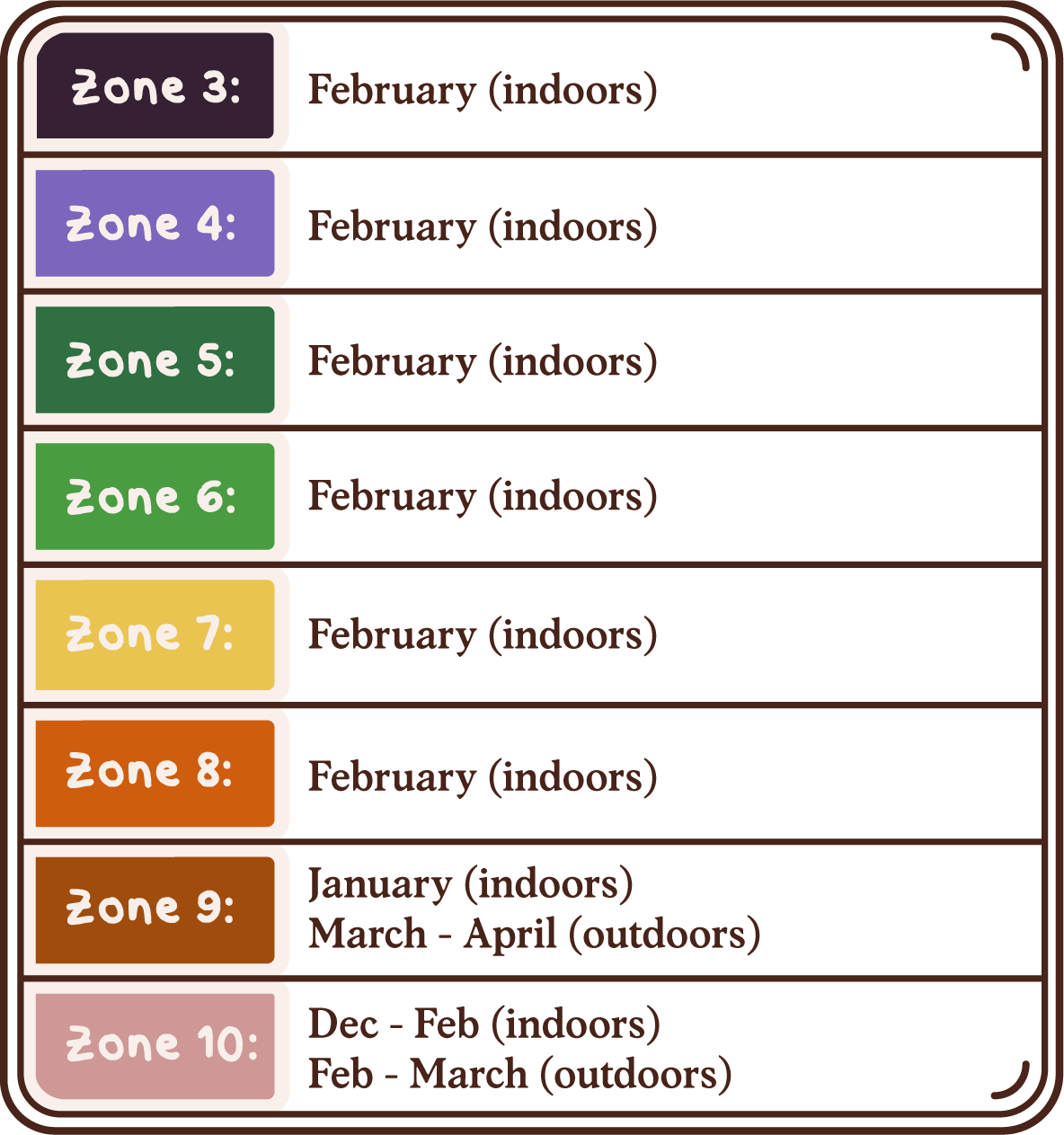
Day to Day Maintenance

-
Watering
Keep soil evenly moist but not soggy. Allow the top inch to dry between waterings to prevent root rot. Water at the base to avoid fungal issues.
-
Pruning
Trim early flowers to direct energy into fruit production. Remove weak or overcrowded branches to improve airflow and encourage healthy growth.
The Harvest

-
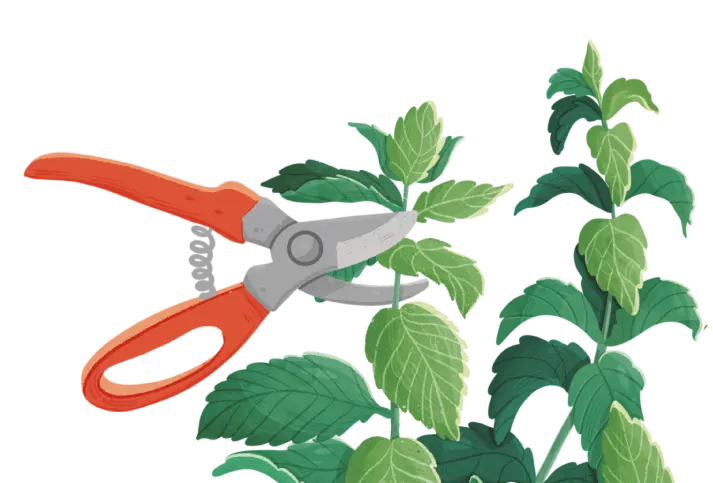
Gathering
Pick ghost peppers when they fully ripen to red, orange, or yellow. The peppers should feel firm to the touch, not soft or mushy. Use scissors or pruning shears to avoid damaging the plant.
-
Wear gloves when harvesting. The capsaicin in these peppers can cause skin irritation and burning. Be sure to wash your hands thoroughly after handling and avoid touching your eyes.
Favorite Uses
-

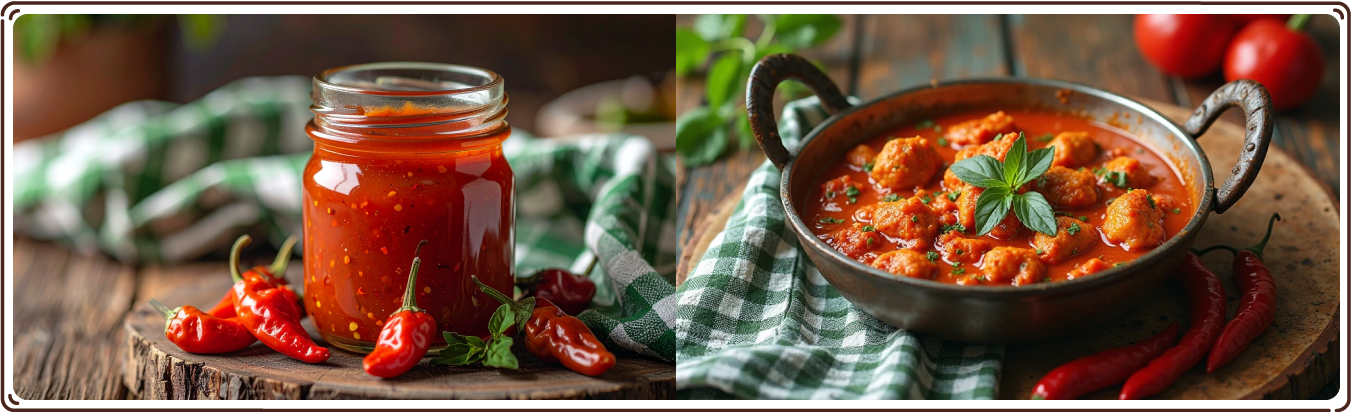
Curry
-

Hot Sauce
-

Chili Oils
-
Salsa
-
Pickles


How to Store
-
Room Temperature
Duration: 3-5 days
Location: Keep on a countertop away from direct sunlight
Method: Store freshly picked ghost peppers in a bowl or paper bag at room temperature. Ensure good air circulation to prevent moisture buildup and spoilage.
-

Refrigeration
Duration: 2-3 weeks
Location: Store in the refrigerator
Method: Place ghost peppers in a breathable paper bag or a perforated plastic bag in the crisper drawer. Avoid sealing them in airtight containers, as trapped moisture can cause rot.
-

Freezing
Duration: Several months
Location: Store in the freezer
Method (Whole Peppers): Wash and dry peppers thoroughly, then place them in a single layer on a baking sheet to freeze before transferring to a freezer-safe bag. This prevents clumping.
-
Drying
Duration: One year
Location: Warm, dry, and well-ventilated area out of direct sunlight
Method: String whole peppers together and hang them to dry, or use a food dehydrator set to a low temperature. Once fully dried, store in an airtight container for long-term use.
Fun Facts

-
Fiery Defense
Ghost peppers contain capsaicin, which not only makes them incredibly spicy but also acts as a natural deterrent against pests and animals.
-
Record Breaker
In 2007, the ghost pepper was officially recognized by the Guinness World Records as the hottest pepper in the world, but it has since been surpassed by the Carolina Reaper and Pepper X.
-
Heat with Purpose
Beyond spice, ghost peppers are used in military-grade pepper sprays and natural pest repellents due to their intense potency.
-
Culinary Daredevil
Despite their heat, ghost peppers are popular in hot sauces, curries, and even spicy desserts for those brave enough to handle the burn.
Subscribe to our Newsletter: "The Small Garden Chronicles"
Where curious growers gather for garden inspiration.













