
GROW GUIDE
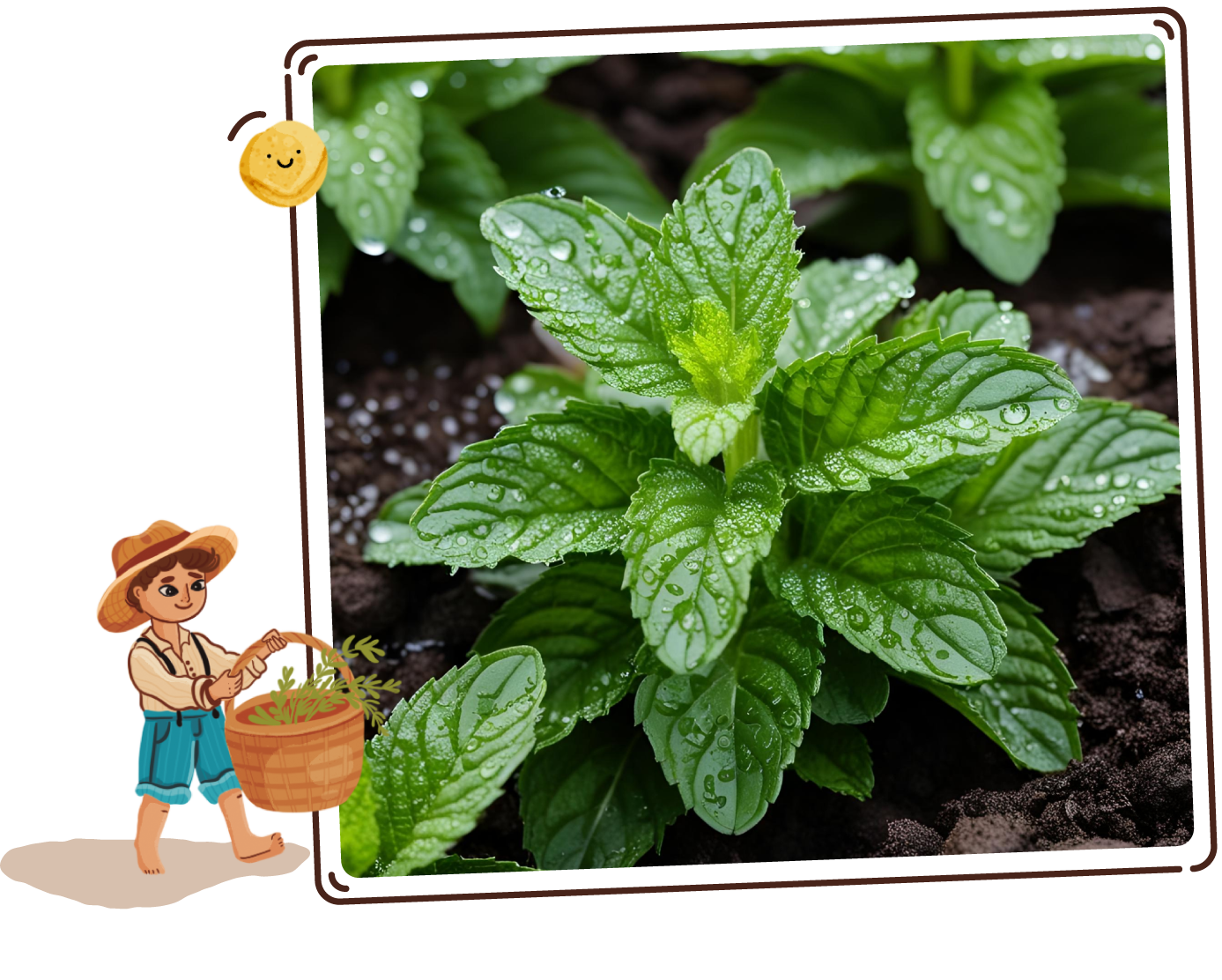
Peppermint
Mentha piperita
Plant Description

Peppermint
A versatile herb with vibrant green, serrated leaves and a refreshing aroma. Known for its cool, sweet flavor, mint is a popular addition to beverages, desserts, and savory dishes alike.
It is celebrated for its invigorating scent and is often used in teas, mojitos, and garnishes, providing a burst of freshness.
Quick Facts:
-

Sun Requirements
Partial to Full Sun
-

Days To Sprout
10-15 Days
-

Days To Harvest
50-70 Days
-

Plant Spacing
18-24"
-

Seeds Per Hole
3
-

Planting Depth
1/4"
Best Planting Locations
-

Windowsills
Ideal for small herbs, providing adequate sunlight.
-

Raised Beds
Contains growth and maintains soil quality.
-

Indoor Planters
Portable and can be moved to optimize sunlight and growing conditions.
-
Containers
Ideal for controlling soil quality and moisture; easy to move.
Getting Started

-
1
Find the Spot
Prefers partial shade over full sun. It's a versatile grower that can thrive in varied lighting conditions, making it suitable for both garden beds and indoor pots.
It can be invasive, so consider planting it in containers or using barriers around garden plantings.
-
2
Prep the Soil & Fertilizer
Mint likes moist, rich soil. Regular watering and a mulch layer can help keep the soil moist. Use a general-purpose fertilizer sparingly to avoid overly vigorous growth.
-
3
Plant the Seeds
Plant 3 seeds in each hole, about 1/4" deep. Sprinkle the small seeds gently into the dirt without totally burying them as they require light to sprout.
During germination, gently mist with water to keep soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged. Maintain a soil temperature between 68° to 75° F. Space plants about 18-24 inches apart.
Good Neighbors:
-

Beans:
Mint protects beans from rodent attacks
-

Broccoli:
Mint helps repel cabbage flies and helps improve the growth of broccoli
-

Cabbage:
Enhances cabbage's flavor, and repels white cabbage moth and flea beetles
-

Carrots:
Mint is a good repellent of the carrot fly, which lays its eggs around the root end of a developing carrot
-

Cauliflower:
Enhances cauliflower flavor, and repels white cabbage moth and flea beetles
Enemy Plants:
-

Chamomile, Oregano & Rosemary:
Mint tends to compete for resources with these plants
Attractants:
-

Bees, Butterflies & Hoverflies:
Mint flowers are a source of nectar
Repellents:
-

Cabbage Moths
Repelled by mint's aroma
-

Mosquitoes
Repelled by mint's aroma
-

Mice
Repelled by mint's aroma
-

Ants
Mint's potent smell masks pheromones that ants use to communicate, disrupting their navigation ability
Best Time to Plant
USDA Hardiness Zones
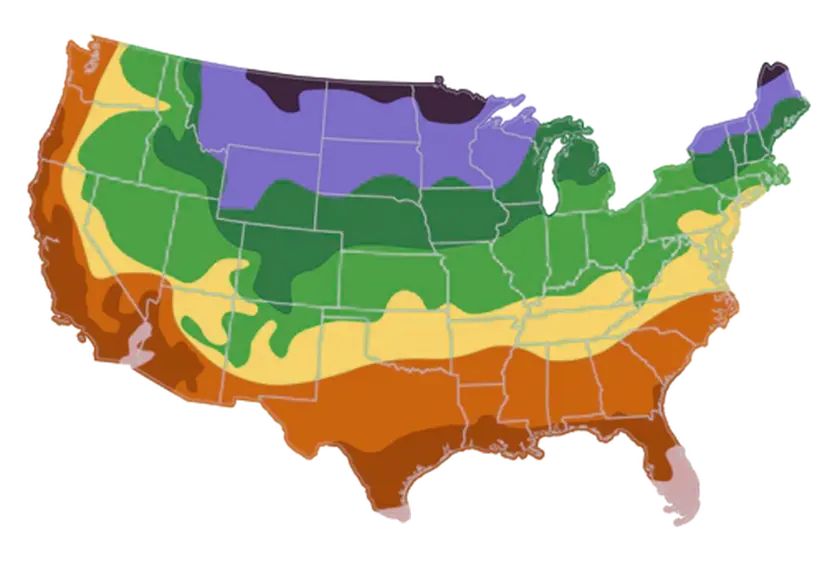
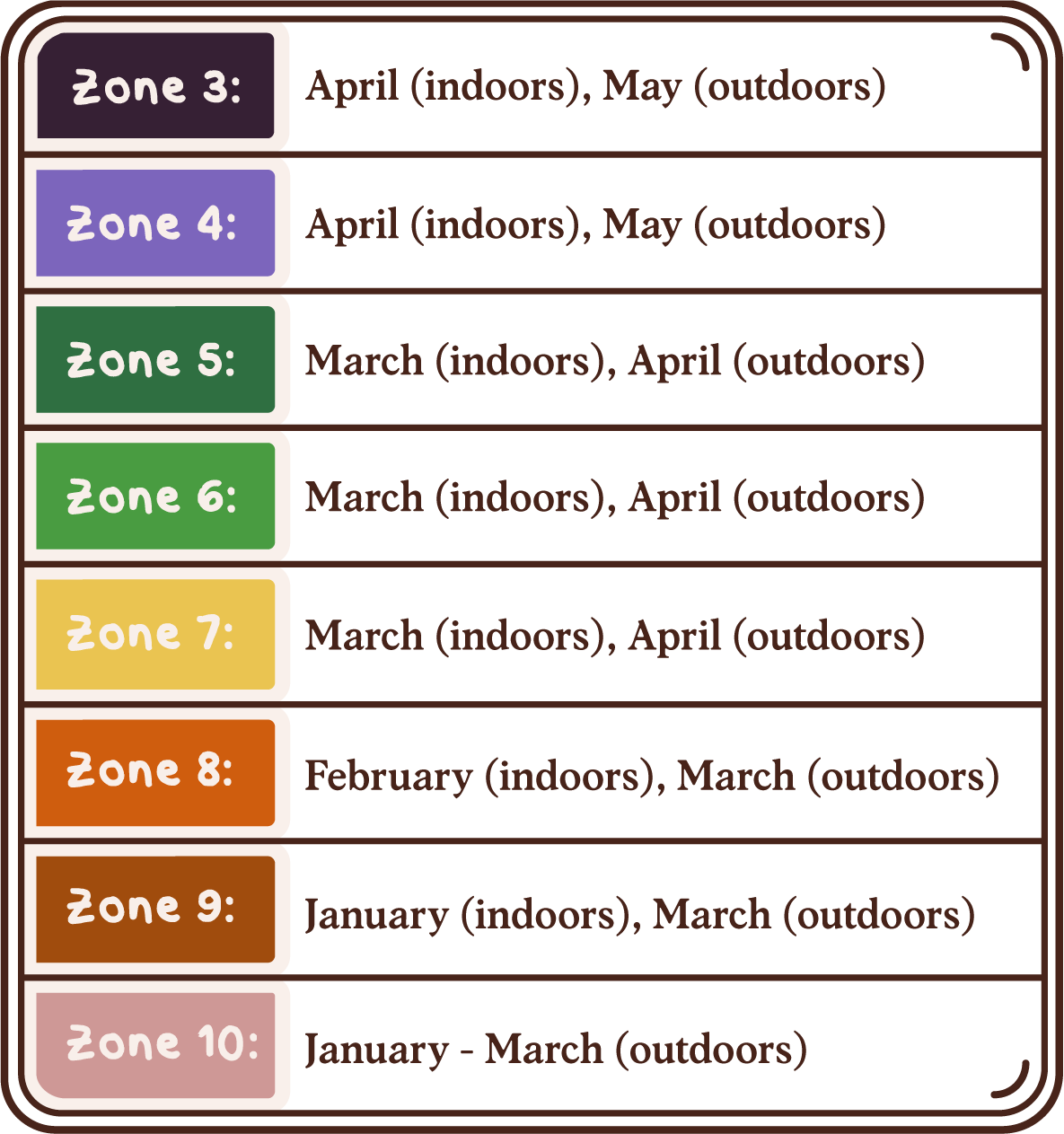
Day to Day Maintenance

-
Watering
Requires consistently moist soil, so water regularly to prevent the soil from drying out. It’s less susceptible to the issues of over-watering than many other herbs, but good drainage is still crucial.
-
Pruning
Frequent harvesting will keep it under control and encourage new growth, making the plant bushier. Pinch off the tips of the stems to promote branching and cut back any runners to keep the plant contained.
The Harvest
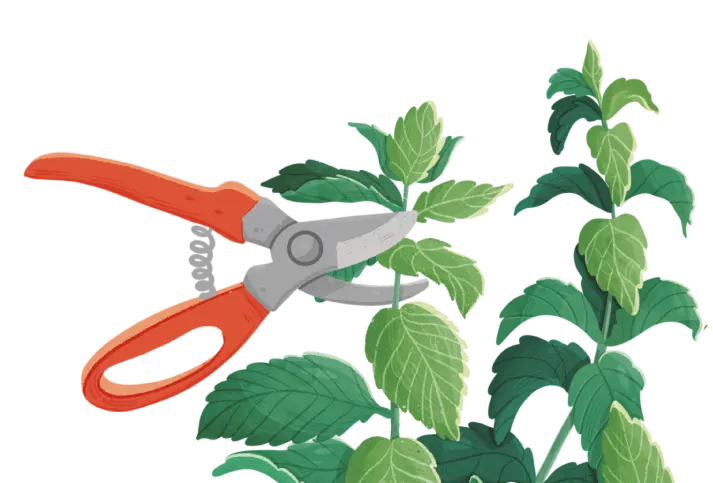

-
Gathering
Pick leaves or sprigs as required. Frequent harvesting is beneficial as it helps to control the growth and spread of the plant.
-
Harvest mint leaves early in the morning to capture the best flavor and aromatic quality.
Favorite Uses
-
Tea
-
Essential Oil
-
Cocktails
-
Salad
-
Lamb


How to Store
-

Refrigeration
Duration: 1-2 weeks
Location: Store in the refrigerator
Method: Place leaves in a damp paper towel and then in a plastic bag. Keep in the crisper drawer to maintain freshness.
-

Freezing
Duration: Several months
Location: Store in the freezer
Method: Chop mint and freeze in ice cube trays with water or olive oil for easy addition to drinks or dishes.
-
Oil Preservation
Duration: Several months
Location: Store in the refrigerator
Method: Submerge chopped mint in olive oil in airtight containers; keep refrigerated and use as needed.
-
Vinegar Preservation
Duration: Several months
Location: Cool, dark place
Method: Place leaves in vinegar to create a flavorful infusion perfect for dressings and marinades.
Fun Facts

-
Ancient Currency
Mint was so valuable in ancient times that it was used as a form of currency in places like Ancient Egypt.
-
Digestive Aid
Mint has long been recognized for its properties as a digestive aid, helping to soothe stomach issues and aid digestion.
-
Versatile Flavoring
Mint is used worldwide in a variety of dishes, from Middle Eastern salads to Indian chutneys and the famous mint julep cocktail.
Subscribe to our Newsletter: "The Small Garden Chronicles"
Where curious growers gather for garden inspiration.












