
GROW GUIDE
Sugar Snap Peas
Pisum sativum
Plant Description
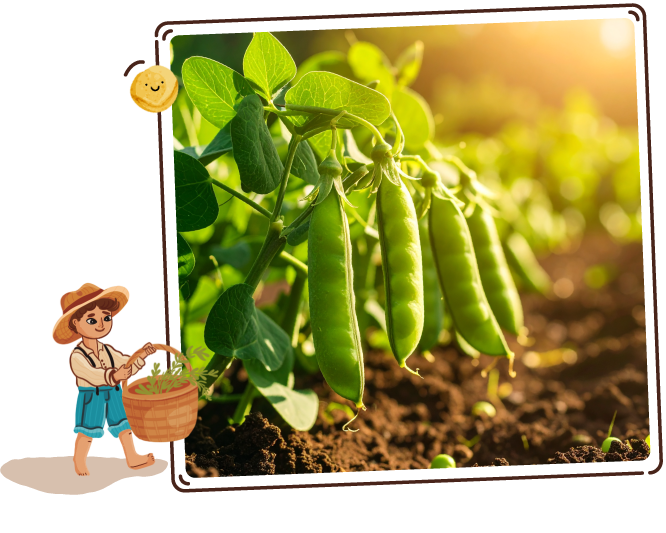

Sugar Snap Peas
A crisp, vibrant legume recognized for its plump, podded shape, with a smooth, slightly curved exterior that snaps cleanly when broken.
This garden favorite, a hybrid of snow and garden peas, is prized for its sweet, juicy crunch, making it a refreshing addition to both raw and cooked dishes.
Quick Facts:
-

Sun Requirements
Full Sun
-

Days To Sprout
7-10 Days
-

Days To Harvest
55-70 Days
-

Plant Spacing
2-3"
-

Seeds Per Hole
2
-

Planting Depth
1"
Best Planting Locations
-

Garden Beds
Perfect for ample space, ensuring deep, well-drained soil for strong root development.
-
Trellised Areas
Ideal for vertical growth, providing support for climbing vines and maximizing garden space.
-

Raised Beds
Offer excellent drainage and soil control, promoting healthy, robust plants.
-

Cool-Weather Zones
Best suited for areas with moderate temperatures, thriving in the early spring or fall.
Getting Started

-
1
Find the Spot
Sugar snap peas thrive in cooler weather with at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Select a spot with some protection from harsh winds to support the climbing vines.
-
2
Prep the Soil & Fertilizer
Use well-draining, loose soil rich in organic matter and mix in some compost. To boost growth, incorporate a balanced fertilizer with a higher phosphorus content and avoid high-nitrogen fertilizers.
-
3
Plant the Seeds
Plant 2 seeds or 1 seedling 1 inch deep in soil or pots. Keep the soil consistently moist, but not soggy, during germination, and ensure the temperature stays between 50° to 70° F.
Once seedlings emerge, thin them to about 2–3 inches apart.
Good Neighbors:
-

Cucumber:
Thrive in the same growing conditions and can share a trellis system
-

Lettuce:
Benefits from the pea's shade and added nitrogen; lettuce helps suppress weeds
-

Mint:
Mint improves health and flavor
-
Radish:
Help deter pests like aphids and beetles
Enemy Plants:
-
Onion, Garlic & Fennel:
Can stunt growth of peas
-

Tomato:
Attracts similar pests
Attractants:
-

Aphids, Spider Mites, Slugs & Weevils:
Feed on the sugar snap pea leaves and sap
Repellents:
-
No known repellents
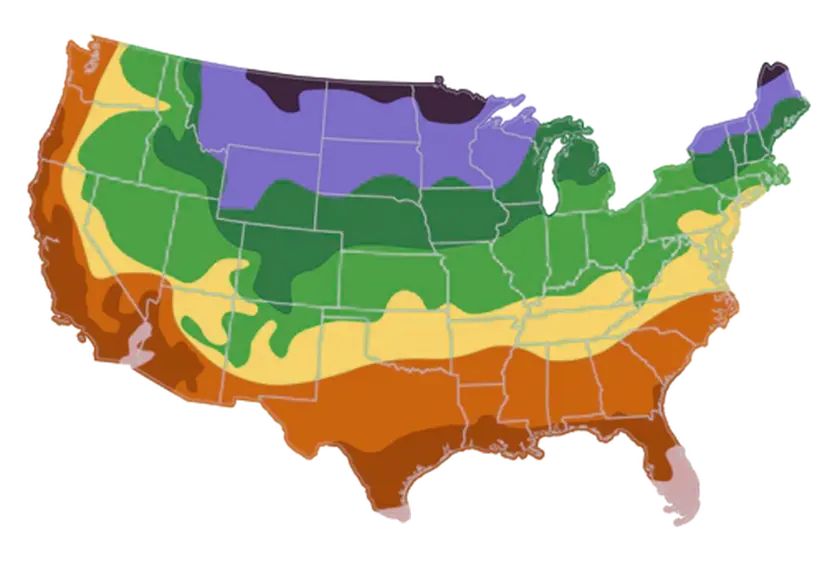
Best Time to Plant
USDA Hardiness Zones
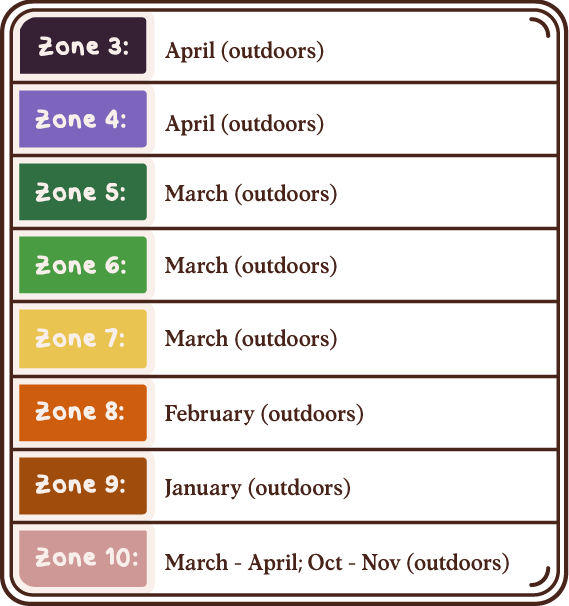
Day to Day Maintenance

-
Watering
Water regularly, ensuring the soil remains moist but not soggy. They thrive with consistent moisture, especially during flowering and pod formation, but avoid overwatering, as it can cause root rot.
-
Support
As the vines grow, provide a trellis or other support to keep the plants upright and off the ground. This helps prevent disease and encourages better air circulation around the leaves and pods.
The Harvest

-
Gathering
Harvest sugar snap peas when the pods are plump, bright green, and tender, but before the peas inside become too large or starchy. Picking regularly encourages more production.
-
For the best flavor and texture, harvest in the early morning when the sugars in the pods are at their peak.
Favorite Uses
-
Snacking
-

Stir-fries
-
Salad
-
Soup
-

Sautéed


How to Store
-
Room Temperature
Duration: 1-2 days
Location: Keep the jar on a countertop away from direct sunlight
Method: Place freshly harvested sugar snap peas in a breathable container like a paper bag or shallow bowl. This helps maintain their crisp texture. Avoid sealing in plastic, as it can cause condensation and lead to spoilage.
-

Refrigeration
Duration: Up to 1 week
Location: Store in the vegetable drawer
Method: Keep peas in a perforated plastic bag or container to allow air circulation. Avoid washing them before storing to prevent moisture buildup, which can cause mold.
-

Freezing
Duration: 6-12 months
Location: Store in the freezer
Method: Blanch sugar snap peas briefly in boiling water, then transfer them to ice water to stop the cooking process. Once cooled, pat dry and spread them out on a baking sheet to freeze individually before placing in a freezer-safe bag or container. This helps maintain their flavor and texture.
-
Drying
Duration: Several months
Location: Warm, dry, and well-ventilated area out of direct sunlight
Method: For long-term storage, sugar snap peas can be dehydrated using a food dehydrator or an oven set to low heat. Store the dried peas in airtight containers in a cool, dark place.
Fun Facts

-
Sweet & Crunchy Snack
Sugar snap peas are a cross between garden peas and snow peas, offering a perfectly crisp texture and a naturally sweet flavor.
-
Lucky Legumes
In some cultures, peas symbolize prosperity and good fortune, making them a common ingredient in New Year's dishes.
-
Climbing High
Sugar snap pea plants love to climb! Given the right support, they can grow over six feet tall, producing an abundant harvest.
-
Fresh from the Pod
Unlike garden peas, sugar snap peas have entirely edible pods, making them a convenient, no-waste snack straight from the vine.
Subscribe to our Newsletter: "The Small Garden Chronicles"
Where curious growers gather for garden inspiration.











